CSIR NET UNIT 1 Notes by Biotecnika – FREE PDF Download
An atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Atoms are composed of three particles i.e. protons, electrons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are present inside the nucleus which account for the mass of the atom. Whereas electrons are present in the space around the nucleus (Fig-1). The number of electrons in the atom is equal to the number of protons. Atoms are extremely small.
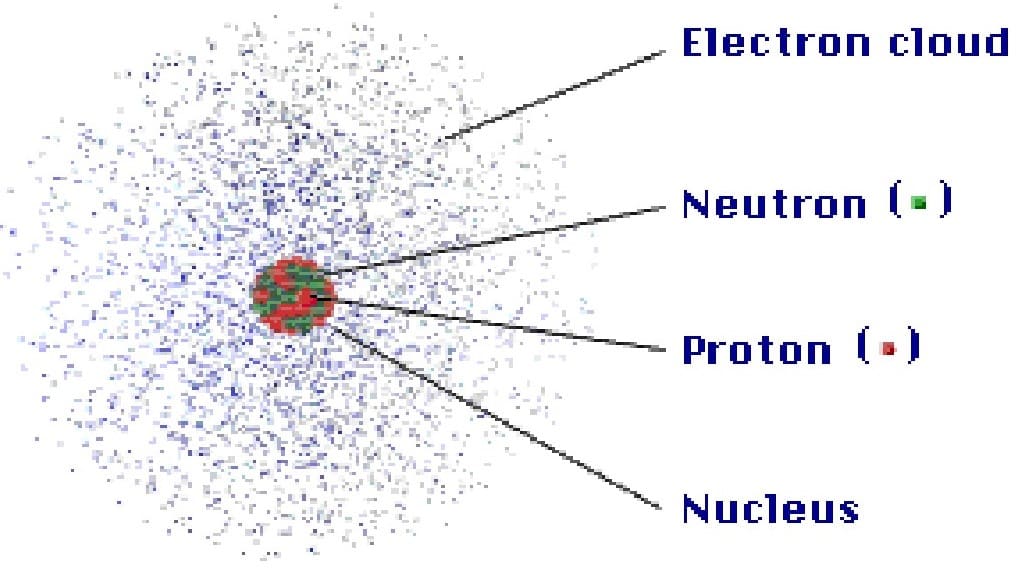
Protons (p+) carry a positive charge with the mass value of 1.672623 x 10-24 g and a relative mass value of 1.007 atomic mass units (AMU) but we can round to 1. Electrons (e–) carry a negative charge with the mass value of 9.110 x 10-28 g and a relative mass value of 0.0005 amu but we can round to 0. Neutrons (no) carry a neutral charge with the mass value of 1.6750 x10 -24 g and a relative mass value of 1.009 amu but we can round to 1 (Fig-2). CSIR NET UNIT 1 Notes by Biotecnika – FREE PDF Download.
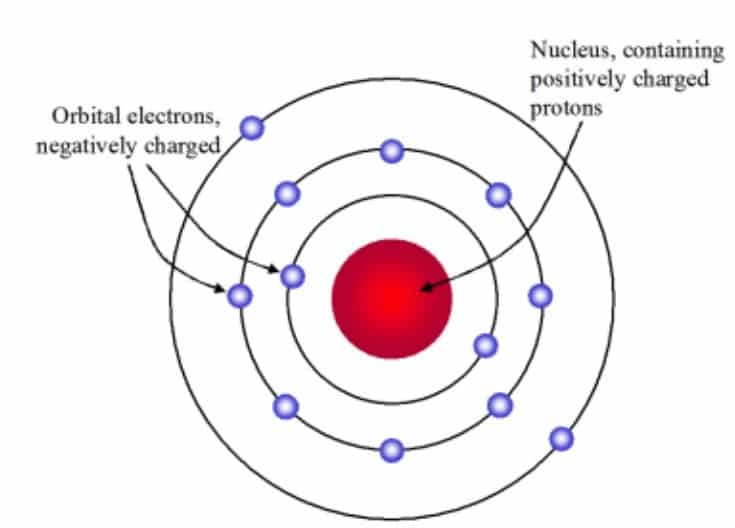
Atoms are consisting of protons and neutrons. Proton is a positive charge and neutron is a neutral charge i.e zero charges there is no charge in it.
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
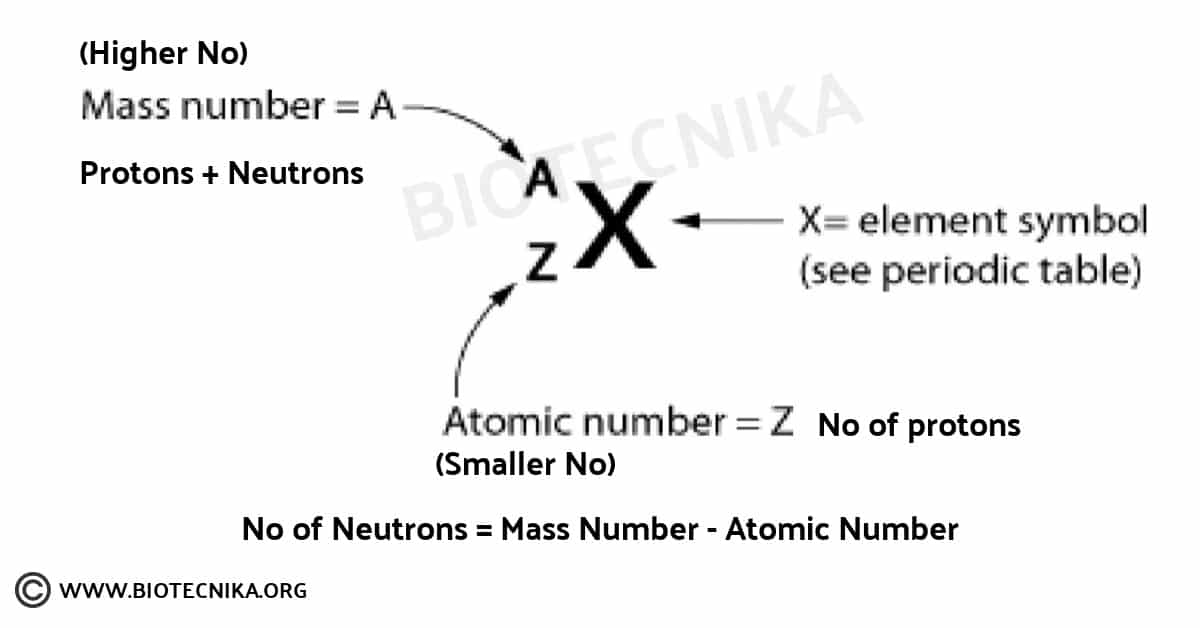
Atomic No, Z – All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons in the nucleus
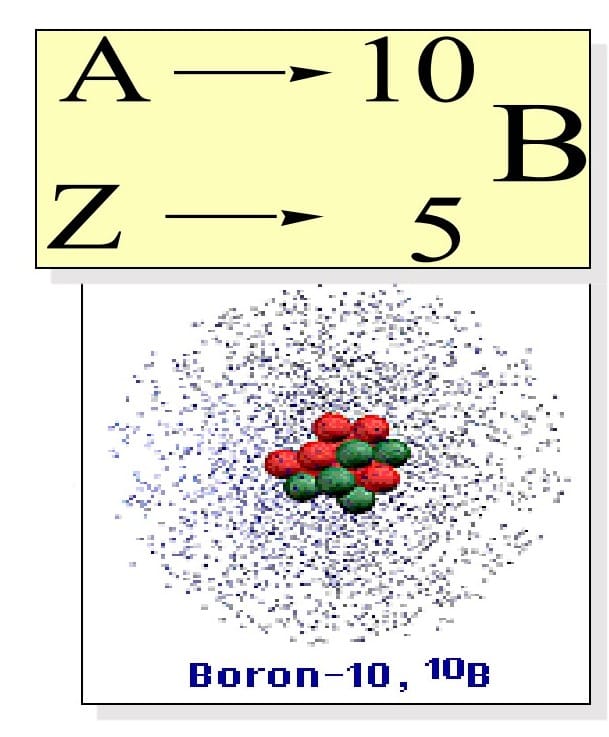
Mass Number, A
- C atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is the mass standard
Fig 4: Boron - = 12 atomic mass units
- Mass Number (A)= # protons + # neutrons
- NOT on the periodic table…(it is the AVERAGE atomic mass
on the table) - A boron atom can have A = 5 p + 5 n = 10 amu
Isotopes
Isotopes are where you have different forms of an element having different neutron numbers because proton numbers cannot change. photon number if it changes the element only will change.
Now, like this many elements will be having isotopes, sometimes isotopes might be a little bit unstable in the nucleus for example, if you’re taking tritium now, how many protons are there in tritium? It’s one only since it’s hydrogen isotope and how many neutrons are there two neutrons are there. If you do three minus one you will get two right. So, three minus 122 neutrons are there and one proton is there which means the neutron is more than the proton. So, this way the nucleus is a bit unstable. CSIR NET UNIT 1 Notes by Biotecnika – FREE PDF Download. So, it wants to give away some of its energy means, it wants to make itself stable by giving away some amount of energy and that is what is called radioactivity.
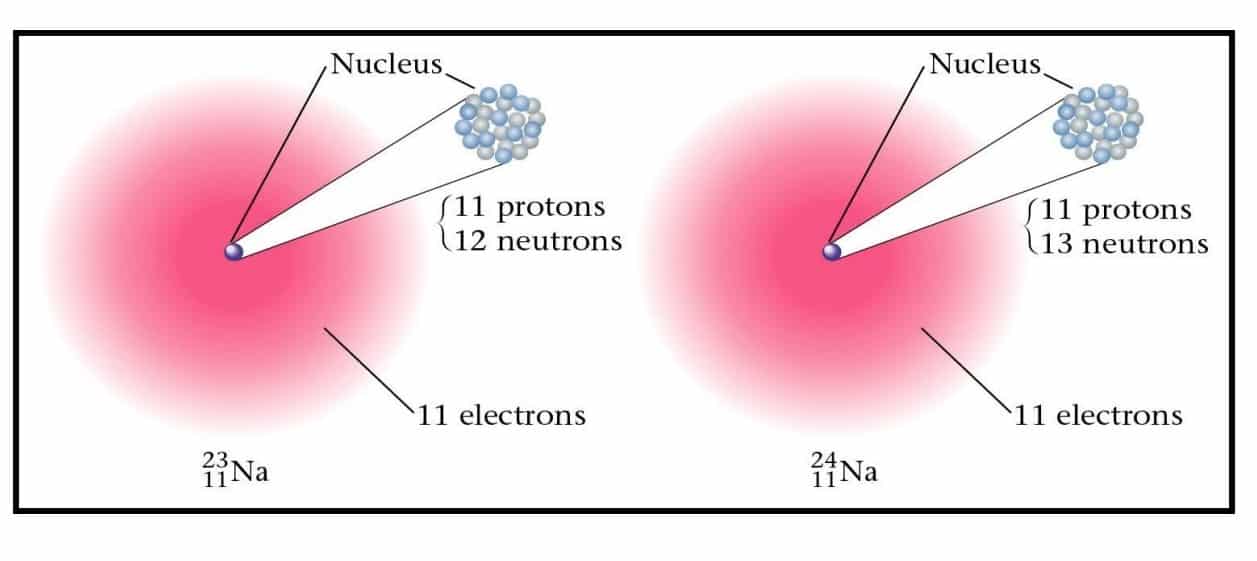
Atoms of the same element (same Z) but a different mass number (A).
• Boron-10 (10B) has 5 p and 5 n
• Boron-11 (11B) has 5 p and 6 n
AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS
Average of all the isotopes that you have you have many isotopes of an element right. So, including all the isotopes whatever will be the total mass number is called the average atomic mass.
For eg: Boron, You will find two types of boron one is 10 boron – the one where you have five protons and five neutrons, and the other boron you see is 11 boron where five protons are fixed but you have six neutrons.
- Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value.
- Boron is 20% 10B and 80% 11B. That is, 11B is 80 percent abundant on earth
- For boron atomic weight = 0.20 (10 amu) + 0.80 (11 amu) = 10.8 amu
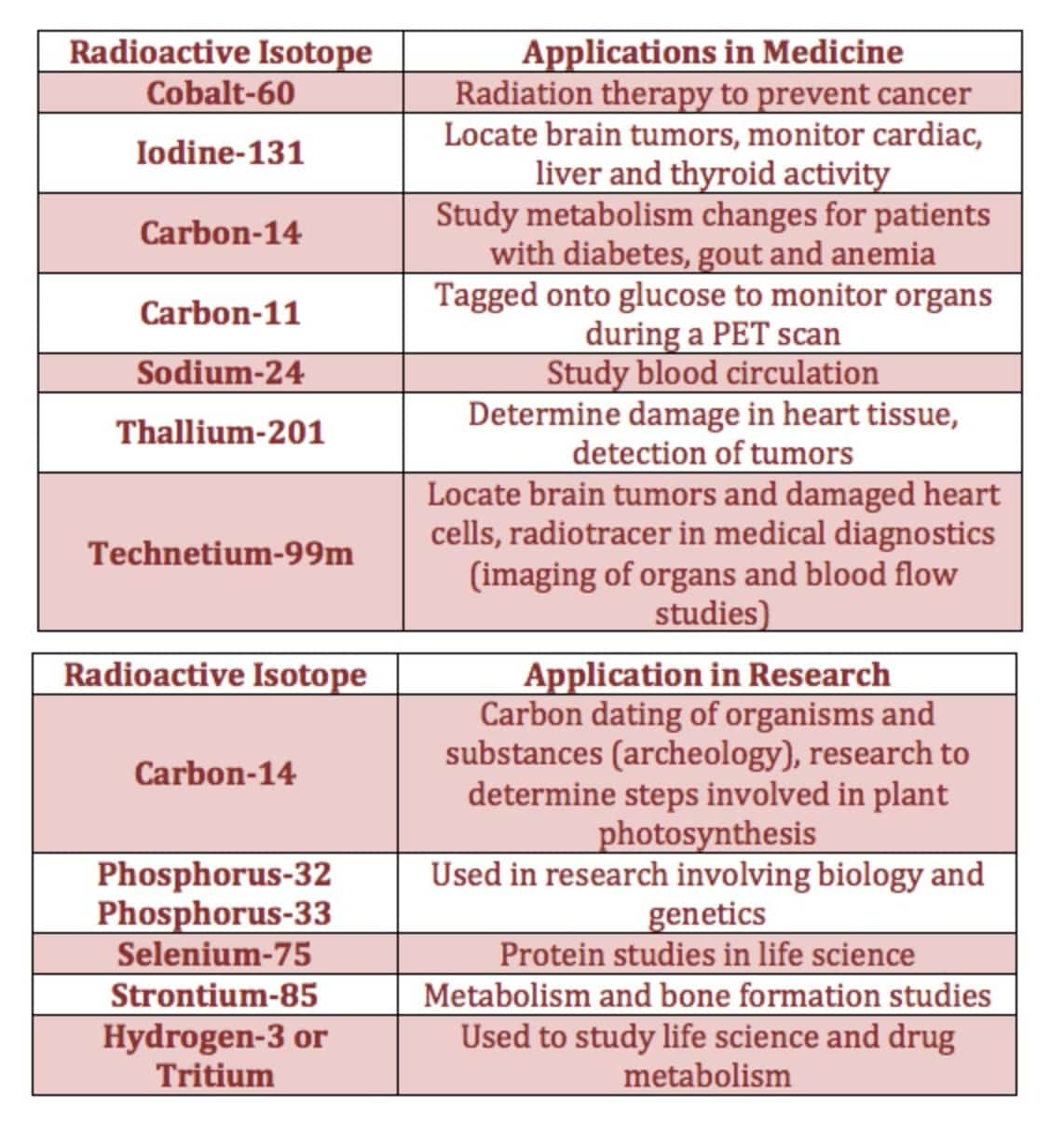
Isotopes & Their Uses
- Radioactive isotopes have an unstable nucleus that decays or emits excess energy or radiation until the nucleus becomes stable. They can be naturally occurring or artificial isotopes of an element. Bone scans with radioactive technetium-99.
- The tritium content of groundwater is used to discover the source of the water, for example, in municipal water or the source of the steam from a volcano.
CSIR UNIT 1 Notes by Biotecnika
Practice Question: From CSIR NET Question Paper of Dec 2016
From the following statements,
A. Hydrogen, Deuterium, and Tritium differ in the number of protons
B. Hydrogen, Deuterium, and Tritium differ in the number of neutrons
C. Both Deuterium and Tritium are radioactive and decay into Hydrogen and Deuterium,
respectively
D. Tritium is radioactive and decays to Helium
E. Carbon-14 decays to Nitrogen-14
F. Carbon-14 decays to Carbon-13
CSIR NET UNIT 1 Notes by Biotecnika – FREE PDF Download.
Pick the combination with ALL correct statements.
1. A, B, and F
2. B, D, and E – Correct Answer
3. A, C, and D
4. C, E, and F
IONS
Ions are atoms or groups of atoms with a positive or negative charge. Taking away an electron from an atom gives a Cation a positive charge. Adding an electron to an atom gives an Anion a negative charge. In order to show the difference between an atom and an ion, the charge is mentioned in the superscript of an ion.
Examples: …
Fill Up the Form & Follow the procedure to download the complete FREE PDF of CSIR NET UNIT 1 Notes
Biotecnika’s Scholarship Program- for CSIR NET & GATE Aspirants
Jumbo Combo Bheem Batch starting on 4th May 2022
No more Excuses!
Claim your scholarship and Get Started with CSIR NET & GATE







































Msc aspirants